The website has the complete lesson note for all the subjects in secondary school but this piece showcases the SS1 Animal Husbandry Lesson Note on Digestion in Domestic Fowl. You can use the website search button to filter out the subject of interest to you.
CLICK HERE to download the complete Document: DOWNLOAD HERE
DIGESTION IN DOMESTIC FOWL
Birds are mono-gastric animals or animals with simple stomachs. The alimentary canal consists of the mouth, oesophagus, crop, proventriculus, gizzard, duodenum, ileum, and colon. Caecum and anus.
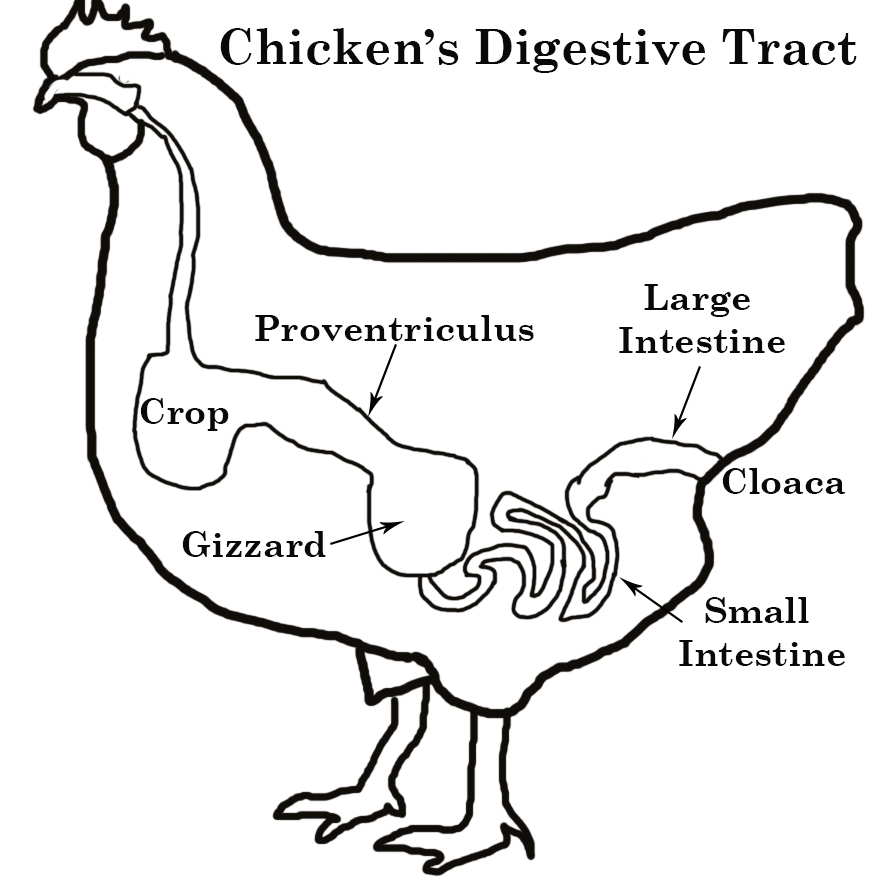
Mouth: Birds have beak which is used to feel and pick up grains (marsh) one after the other. The tongue aids in swallowing food into the oesophagus.
Crop: This is a sack-like structure used for the temporary storage of food. Certain bacteria present here help in fermenting and moistening the food. The fermented food then leaves here through the oesophagus into the proventriculus.
Proventiculus: This is the first part of the stomach. Here gastric juice which is acidic due to the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid contains the enzyme pepsin which acts on protein and converts it into peptone.
Gizzard: This act as the teeth of birds. It helps in the mastication and chewing up of food substances. The gizzard is a tough, thick and muscular organ which contains pebbles or stones that aids the grinding of food. Bile juice from the liver is mixed up with the food substances.
Caecum: This harbours micro-organisms which aid the breaking down of some cellulose into glucose.
Cloaca: This is a common part for reproduction and excretion/egesting of waste product.
Subtopic 2
DIGESTION IN RUMINANT
TOPIC: DIGESTION IN RUMINANT
Click on the Downloadable Button to get the FULL NOTE



