The website has the complete lesson note for all the subjects in secondary school but this piece showcases the SS1 Chemistry Lesson Note on Nucleon Number. You can use the website search button to filter out the subject of interest to you.
CLICK HERE to download the complete Document: DOWNLOAD HERE
ATOMIC NUMBER AND MASS NUMBER (NUCLEON NUMBER)
ATOMIC NUMBER:
DEFINITION: Atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of an element.
The atomic number of an element is a whole number and is designated z. In a neutral atom the number of protons must be equal to the number of electrons (since protons are positively charged and electron are negatively charged).
All the atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in their nuclei (i.e. they have the same atomic number). NO two elements have the same number of protons in their atoms.
DEFINITION:
MASS NUMBER (NUCLEON NUMBER): The mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom of an element.
Mass number is represented by the letter A.
Mass number A = Number of protons + number of neutrons.
i.e. A =p + n. Where p=protons, n= neutrons.
Or number of neutrons n =A – Z.
An atom of an element can be described by writing its symbol together with its atomic number and mass number.
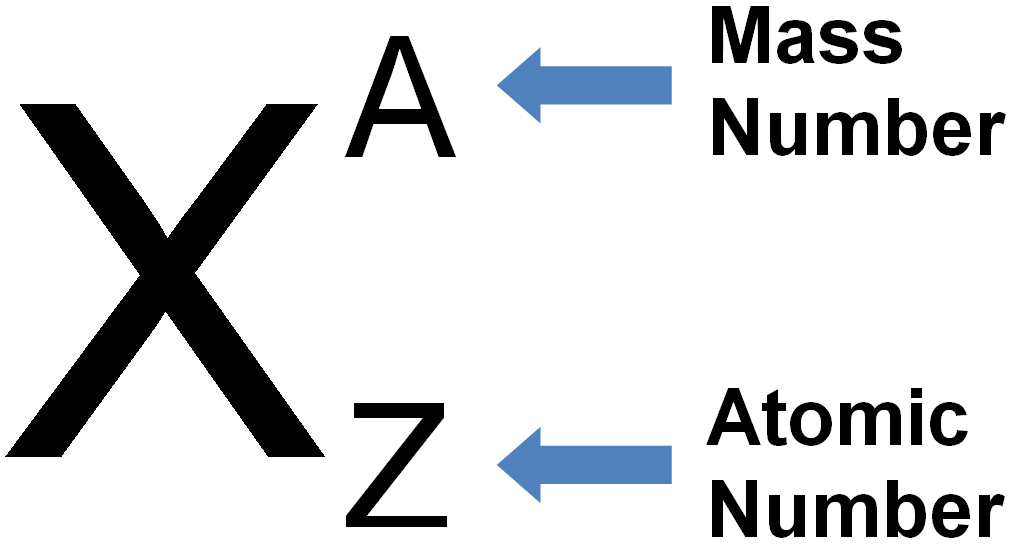
Examples: The atom of carbon, oxygen and sodium can be written as 126C, 168O and2311Na respectively.
EVALUATION:
(1) Define the following: (a) Atomic number (b) Mass number.
(2) Describe the atoms of the following elements using their symbol, atomic number and mass number: (a) Phosphorus (b) Silicon (c) Calcium
PERIODS 3 AND 4: ISOTOPY AND RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS
Definition: Isotopy is a phenomenon whereby atoms of an element exhibit different mass number but have the same atomic number.
Mass spectrometric studies show that the atoms of most elements exist in more than one form. This is due to the difference in number of neutrons present in these atoms. Such atoms are known as isotopes. Isotope of an element is represented by the original symbol of the element with the mass number and atomic numbers. For example, 126C, 136C, 146C represent atoms of the isotopes of carbon. For each atom, the number of neutrons can be obtained by finding the difference between the mass number A and the atomic number Z i.e. A – Z. Each isotope of an element has its own mass known as isotopic mass.
Isotopes of an element have slightly different physical properties because neutrons contribute only to the mass of an atom and not its chemical behaviour. But isotopes of an element exhibit the same chemical properties because the number of valence electrons in an atom of an element determines its chemical behaviour (properties) and since isotopes have the same number of valence electrons they will be chemically alike.
NOTE:
(i) An analysis of the chlorine isotopes.
Isotope 3517Cl Isotope 3717Cl
Click on the Downloadable Button to get the FULL NOTE




