The website has the complete lesson note for all the subjects in secondary school but this piece showcases the SS1 Chemistry Lesson Note on Laws of Chemical Law of Multiple Proportions. You can use the website search button to filter out the subject of interest to you.
CLICK HERE to download the complete Document: DOWNLOAD HERE
LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS
This law states that if two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one of the elements which separately combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in simple ratio.
VERIFICATION OF THE LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS
Some elements form more than one compound, depending on the conditions of the reaction and the valency copper forms. Copper (I) and copper(II) with oxygen. Also in an insufficient supply of air, carbon burns to form carbon(II) oxide and when the supply of air is sufficient, carbon(iv) oxide is obtained.
The sample of the copper (I) oxide and copper(II) are placed in porcelain, boats and placed in a combination tube as in the diagram below.
A current of dry hydrogen is passed through the combustion tube until the oxides are reduced to metallic coppers. They are now cooled and weighed and the masses of copper and oxygen are determined in the two samples.
| Calculations
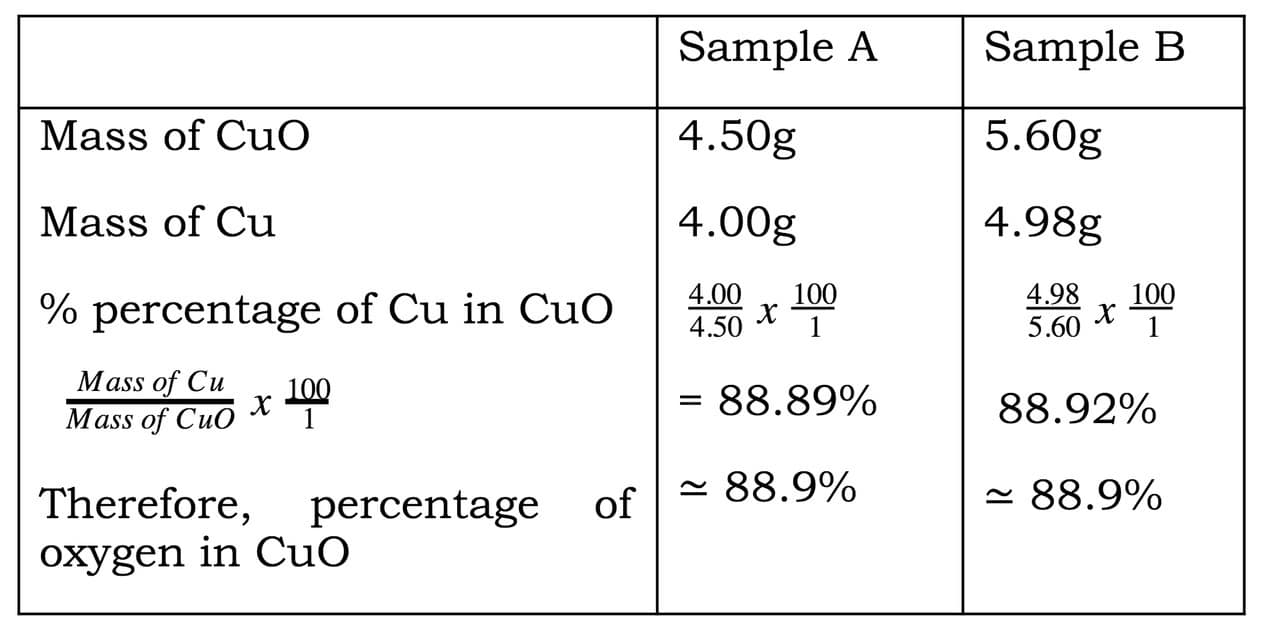
|
Sample A | Sample B |
| (i)Mass of porcelain boat | 4.55g | 5.38g |
| (ii) Mass of porcelain boat + copper oxide | 6.44g | 8.21g |
| (iii) Mass of copper oxide | 1.89g | 2.83g |
| (iv) Mass of porcelain boat + copper | 6.05g | 7.90g |
| (v) Mass of copper (iv) – (i) | 1.50g | 2.52g |
| (vi) Mass of oxygen (iii) –(v) | 0.39g | 0.31g |
For example A1.50g of copper combines with 0.39 of oxygen.
100g of copper combines with × 100 = 26g
For sample (b) 2.52g of copper combines with 0.31g of oxygen
100g of copper combines with × 100= 12.3g
From these calculations, the masses of oxygen (26g and 12.3g) which combine with a fixed mass (100g) of copper are in simple ratio 2:1
Click on the Downloadable Button to get the FULL NOTE




