The website has the complete lesson note for all the subjects in secondary school but this piece showcases the SS1 Chemistry Lesson Note on Coal and Types of Coal. You can use the website search button to filter out the subject of interest to you.
CLICK HERE to download the complete Document: DOWNLOAD HERE
COAL AND TYPES OF COAL
COAL: This is one the two most principal sources of fuel and energy, the other being petroleum. Coal was found as a result of complex chemical and physical changes when the remains of forest were buried under the earth millions of years ago under great pressure in the absence of air.
Coal is found in great abundance in very many parts of the world including Nigeria. Coal is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons (compounds of carbon and hydrogen) and other organic and inorganic compounds containing small amounts of nitrogen, sulphur and phosphorus as impurities.
Types of Coal
Coal is derived from wood; it naturally contains a lot of carbon. There are four main types of coal, arising from the progressive variation in their carbon content. They are:
- Peat-like coal: contains about 60 of carbon.
- Lignite coal: contains about 70 of carbon.
- Bituminous coal: contains about 85 of carbon. This is the type that is mostly used for our everyday domestic application.
- Anthracite coal: contains about 94 of carbon.
The carbon content of each type of coal reflects its rank or degree of classification. Based on carbon content, the different types of coals are put into ranks as follows: Peak → Lignite → Bituminous → Anthracite
Coal is used mainly as a fuel to generate power for station engines, factories and electric parts. It is also used for making various chemicals.
EVALUATION. Carbon occurs most abundantly both naturally as _________ and ______
- With two equations only, describe the combustion of carbon allotropes.
- Mention four types of coal
PERIOD 4: DESTRUCTIVE DISTILLATION OF COAL AND GASIFICATION OF COAL
DESTRUCTIVE DISTILLATION OF COAL
Destructive distillation of coal involves heating of coal to a very high temperature (600—1200o C ) in the absence of air. During the process, coal decomposes to give coal gas, coal tar, ammoniacal liquor and coke as the main products.
Coal + heat → coal gas + coal tar + ammoniacal liquor + coke
The process is also known as industrial distillation of coal. The destructive distillation of coal can be carried in the laboratory using the set up below.
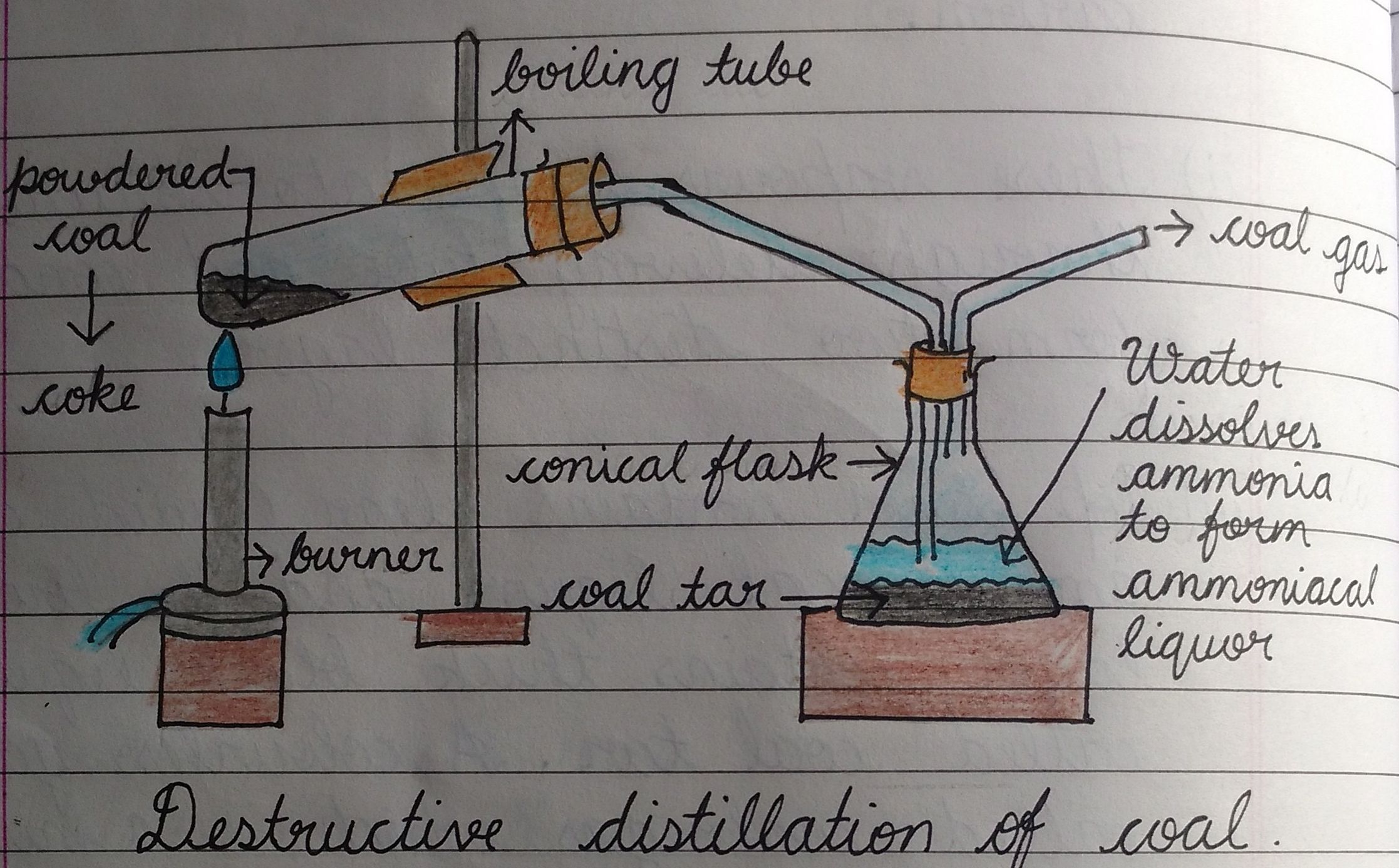
Uses of product of destructive distillation of coal
- Coal gas: Coal gas is a gaseous mixture of hydrogen, methane, carbon (ii) oxide and small amount of ethane, hydrogen sulphide and Sulphur (iv) oxide. The main use of coal gas is as fuel. It is cleaner and more efficient than coal and solid or liquid fuel.
- Coal tar: Coal tar, a thick brownish-black liquid, is a mixture of many organic chemicals including benzene, toluene, phenol, naphthalene and anthracene. The components can be separated by fractional distillation and are used for the manufacture of commercial products including drugs, dye, paints, insecticides, explosives, etc.
- Ammoniacal liquor: This an aqueous solution containing mainly ammonia and is used in the manufacture of ammonium tetraoxosulphate(iv), (NH4)2SO4 .
- Coke: Coke is non-volatile residue which contains about 90 of amorphous carbon and is chemically similar to hard coal. Coke is used in the manufacture of carbide, as a fuel and as a reducing agent in the extracting of metals. Coke is used to make producer gas and water gas through a process called gasification.
Uses of Coke
Click on the Downloadable Button to get the FULL NOTE



